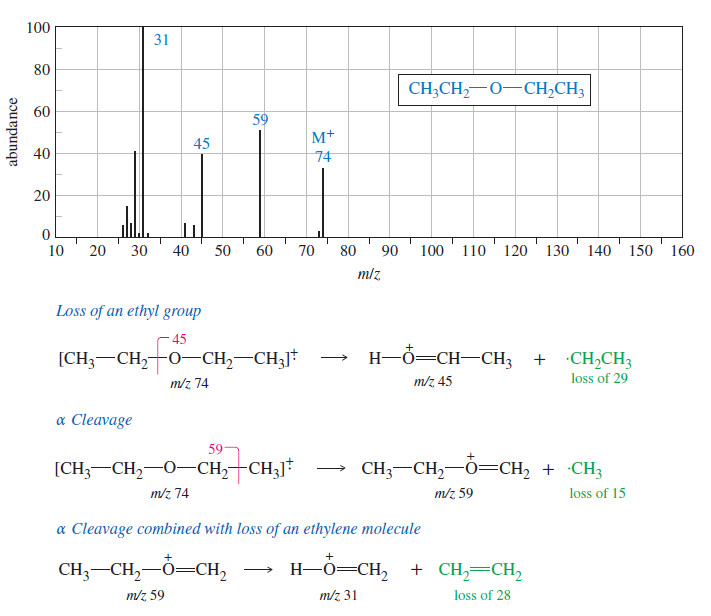
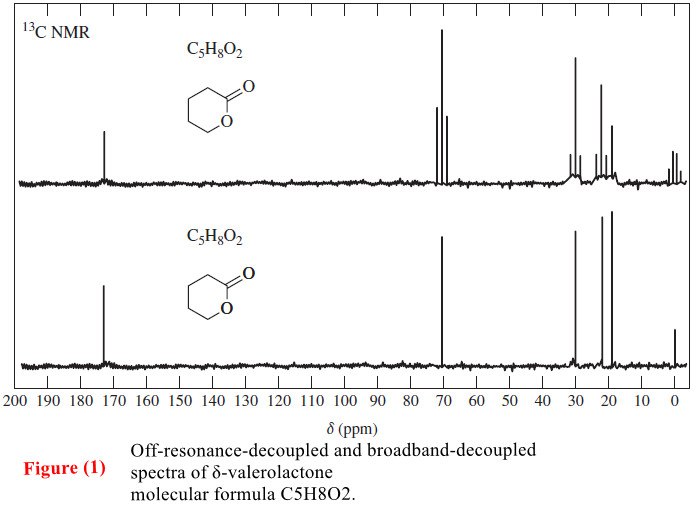
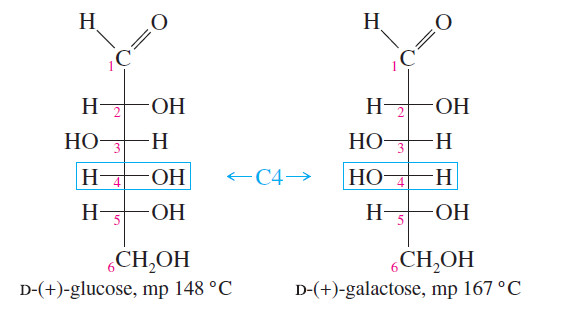
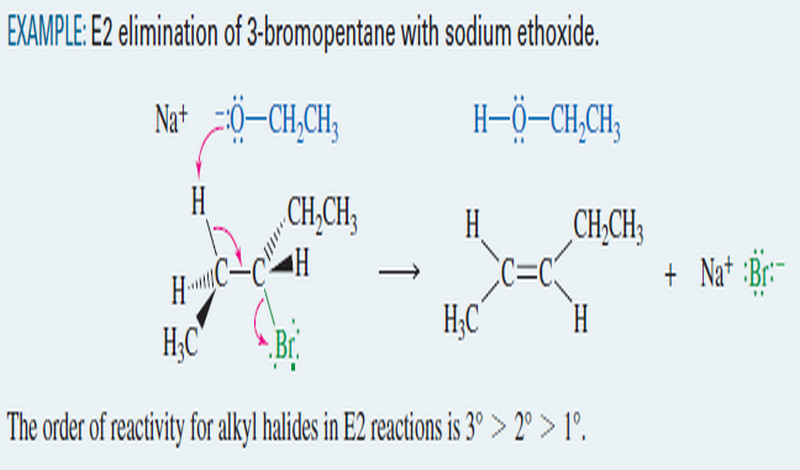
Popular Posts
-
General Chemistry
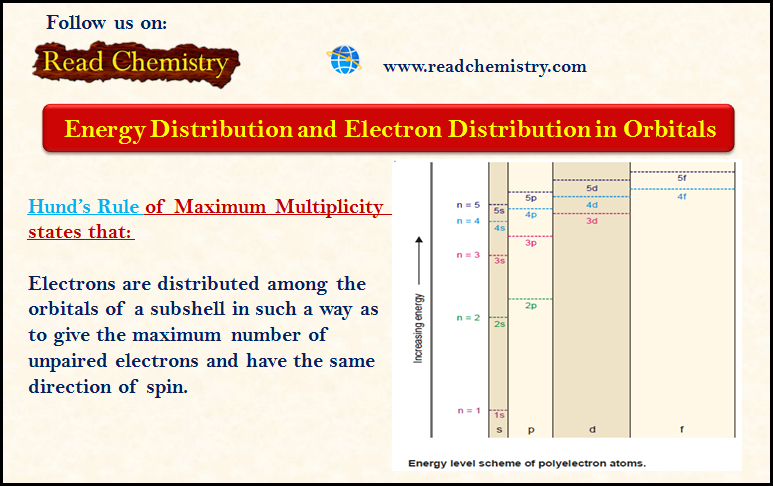
Distribution of Electrons in Orbitals
– In this subject, we will discuss the Distribution of Electrons in Orbitals according to Hund’s Rule. Energy Distribution and…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
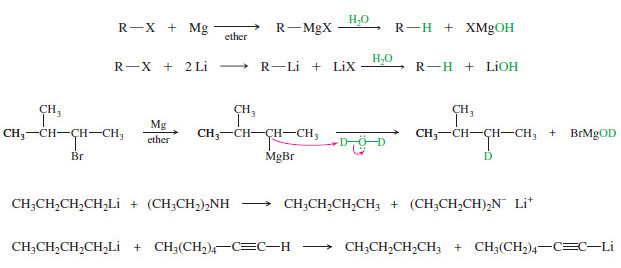
Side Reactions of Organometallic Reagents
Side Reactions of Organometallic Reagents: Reduction of Alkyl Halides – Organometallic Reagents: Grignard and organolithium reagents are strong nucleophiles and…
Read More » -
Analytical Chemistry
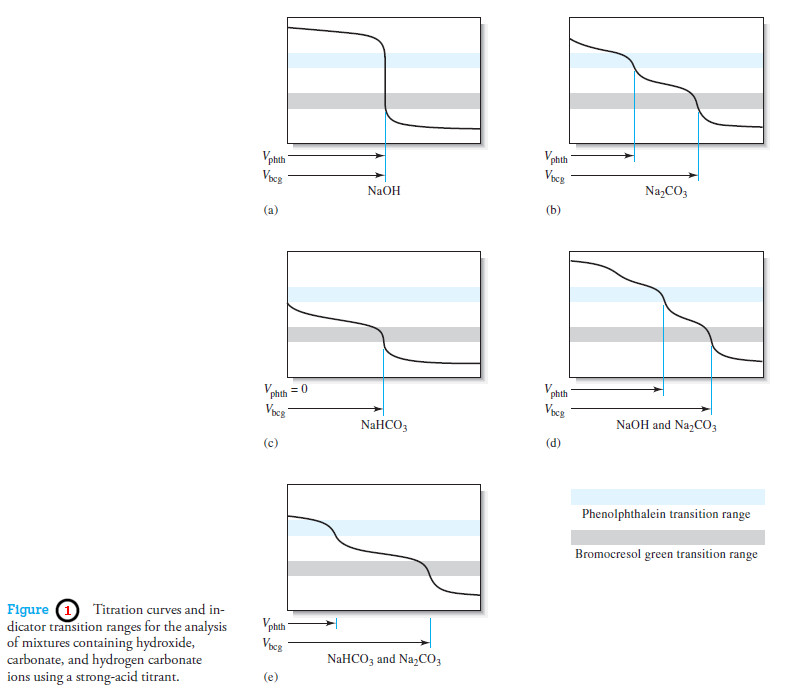
Applications of Neutralization Titrations
– In this topic, we will discuss The Applications of Neutralization Titrations. Typical Applications of Neutralization Titrations – Neutralization titrations…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
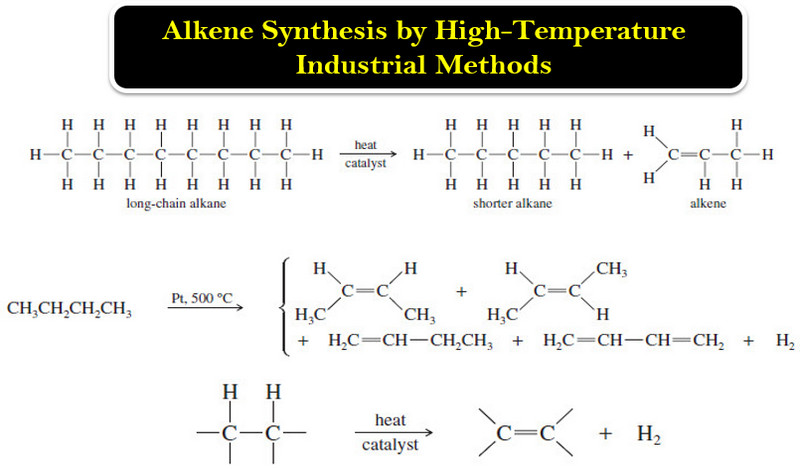
Alkene Synthesis by High-Temperature Industrial Methods
Alkene Synthesis by High-Temperature Industrial Methods (1) Catalytic Cracking of Alkanes – The least expensive way to make alkenes on…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
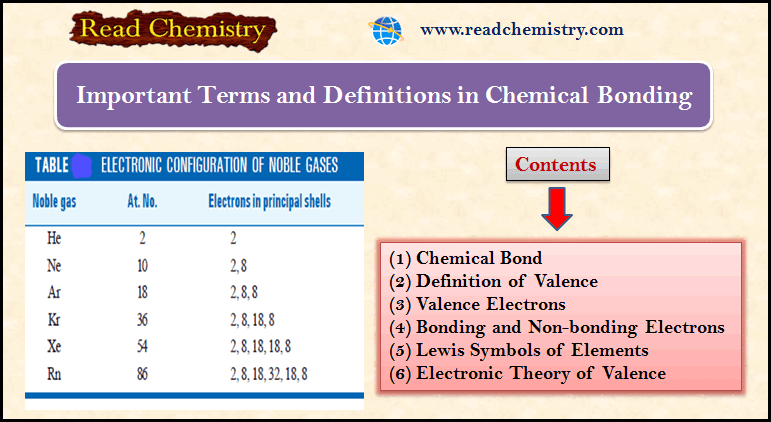
Chemical Bonding: Important terms and Definitions
– In this subject, we will discuss the important Terms and Definitions of Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bond – Molecules of…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
Physical Properties of Alkenes
Physical Properties of Alkenes (1) Boiling Points and Densities – Most physical properties of alkenes are similar to those of…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
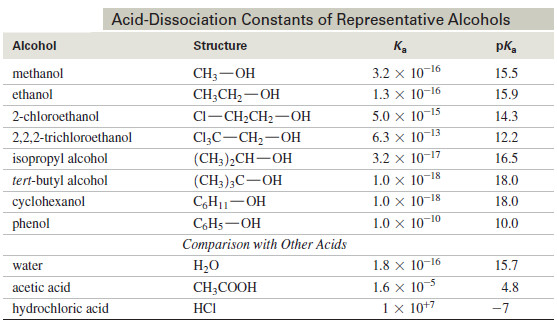
Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols
Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols – we will talk here about some Acidity of Alcohols…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
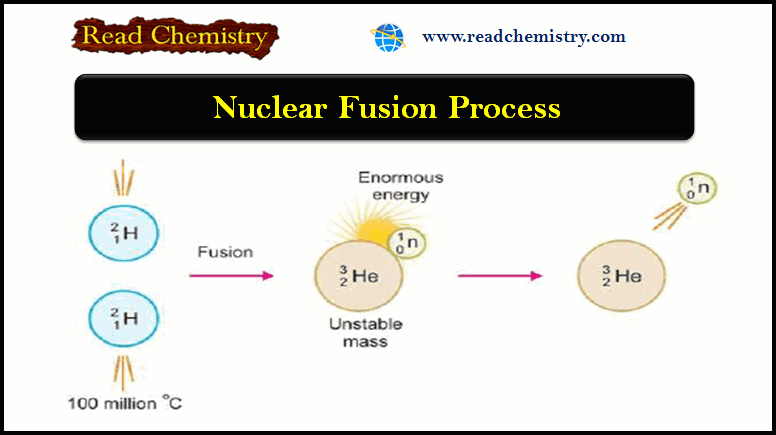
Nuclear Fusion: Definition, Occurrence, Examples, Applications
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Fusion Process ( Definition, Occurrence, Examples,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Fundamentals of Chemistry book by Romain Elsair – Free download
– In this subject, we will discuss the free download of Fundamentals of Chemistry book…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Analytical Chemistry
Reagents for Neutralization Titrations
– In this subject, we will discuss the Reagents for Neutralization Titrations. Reagents for Neutralization…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
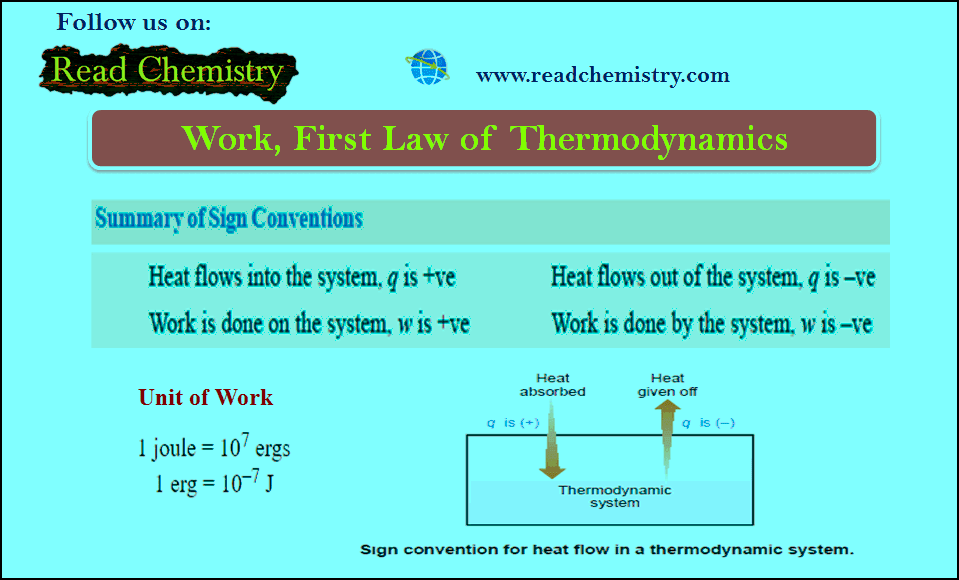
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-