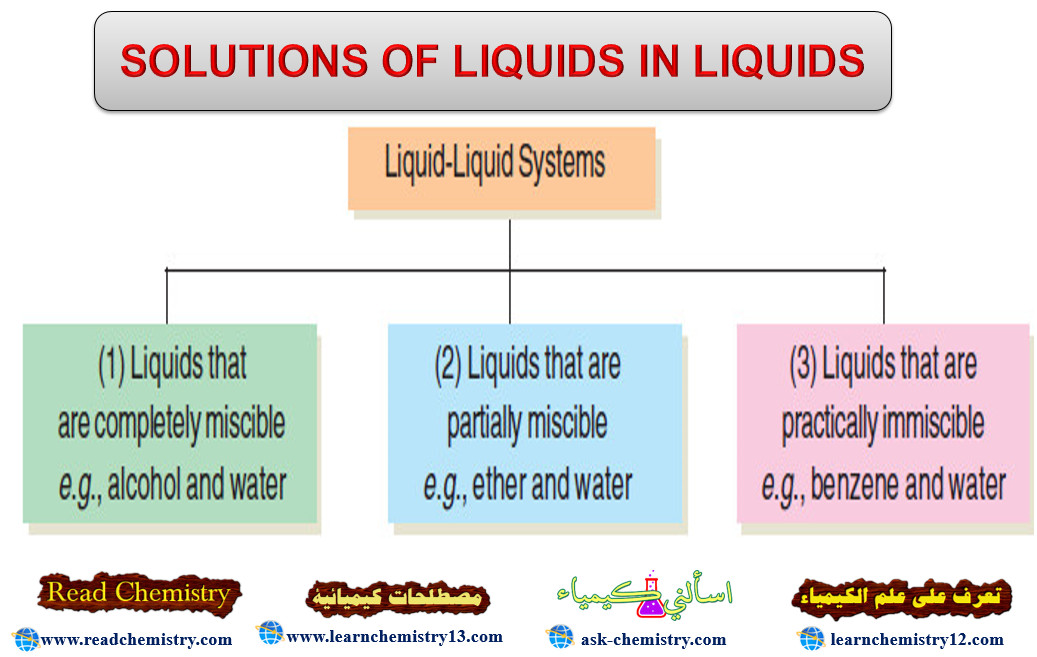
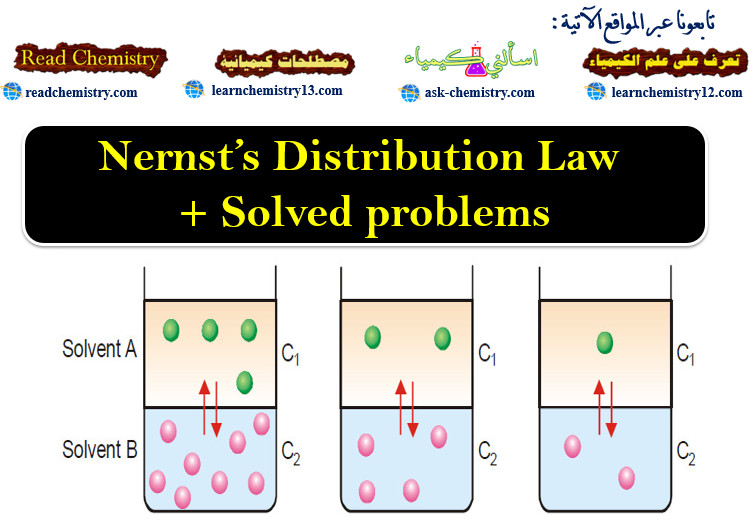
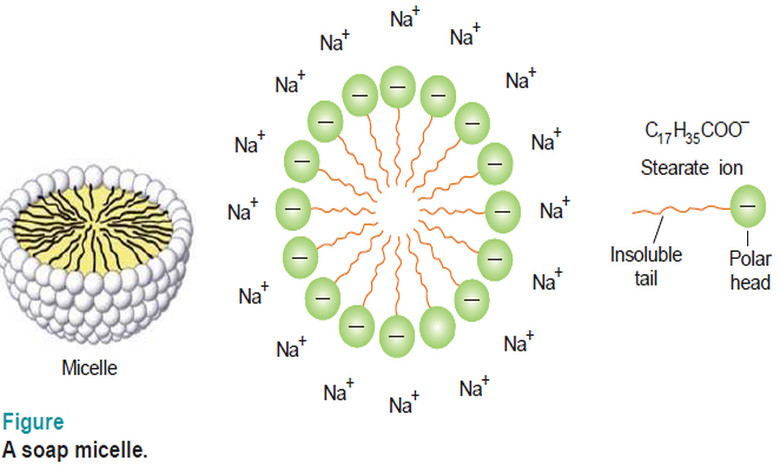
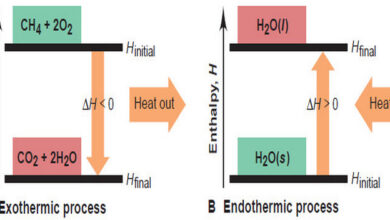
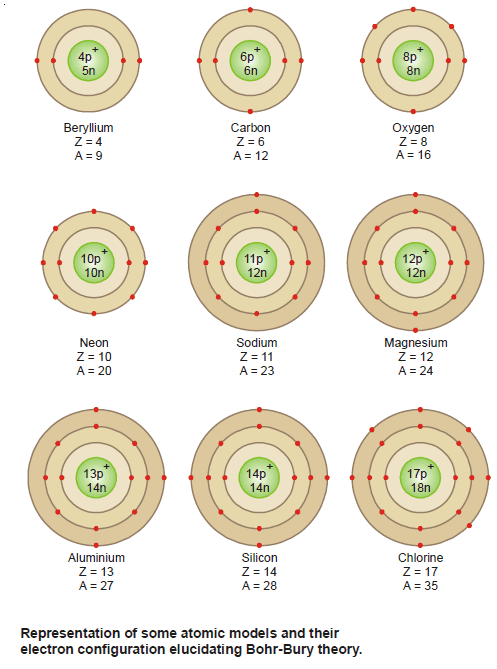
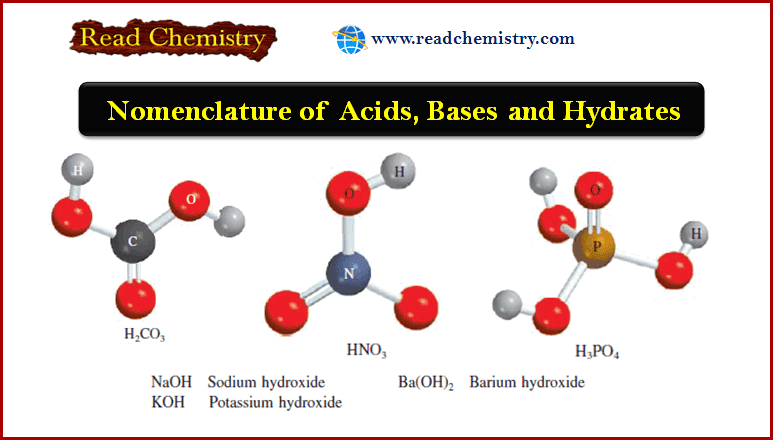
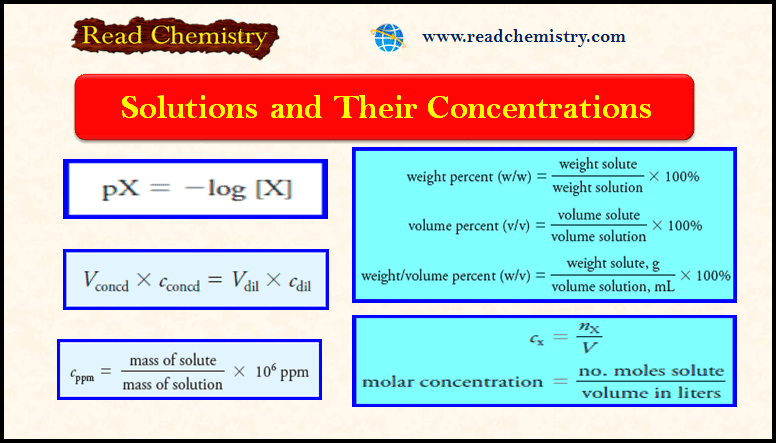
Popular Posts
-
Organic Chemistry
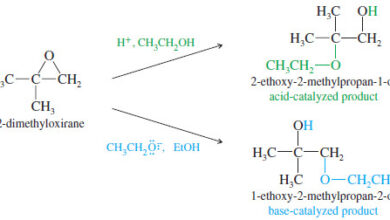
Ring Opening of Epoxides
– In this topic, we will talk aboutAcid-Catalyzed Ring Opening of Epoxides, Base-Catalyzed Ring Opening of Epoxides, and Orientation of…
Read More » -
Analytical Chemistry
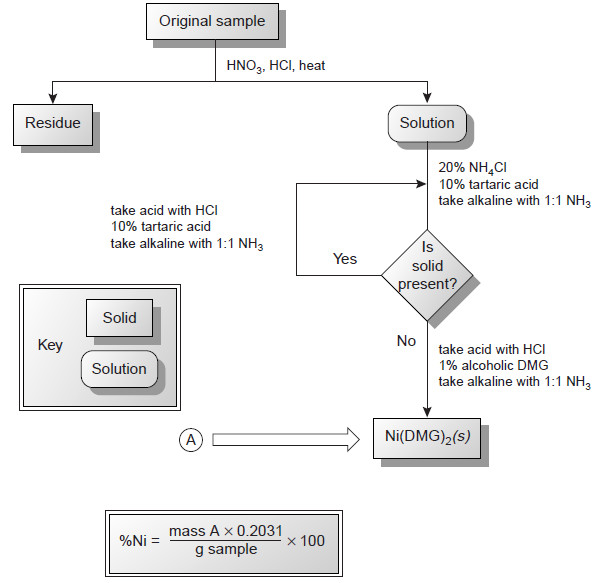
What is Analytical Chemistry?
What is Analytical Chemistry? Analytical chemistry is what analytical chemists do. – Analytical chemistry is too broad and active a…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
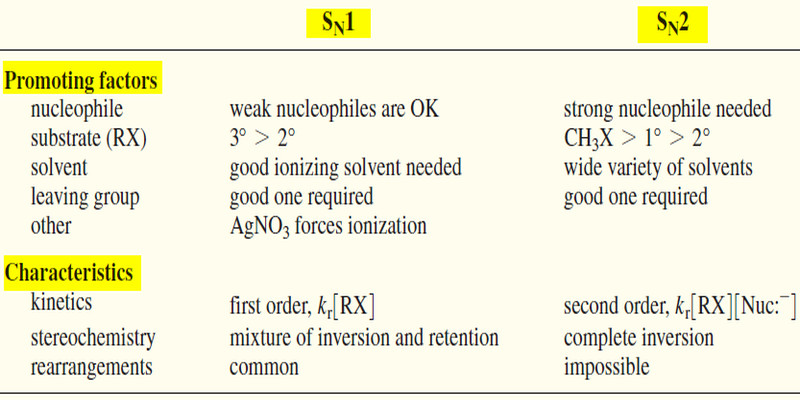
Comparison of SN1 and SN2 Reactions
Comparison of SN1 and SN2 Reactions Let’s compare what we know about the SN1 and SN2 Reactions and reactions, the…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
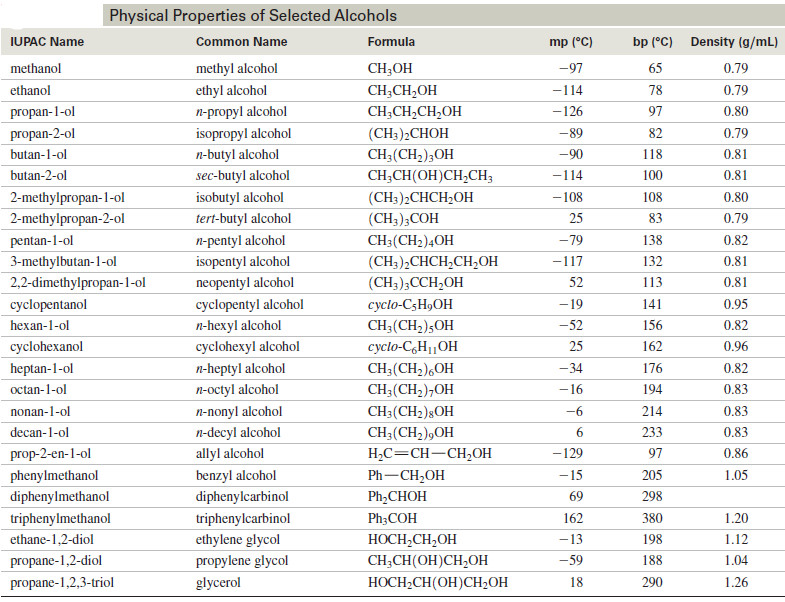
Physical Properties of Alcohols
We will discuss here Physical Properties of Alcohols: (A) Boiling Points of Alcohols (B) Solubility Properties of Alcohols Physical Properties…
Read More » -
Analytical Chemistry
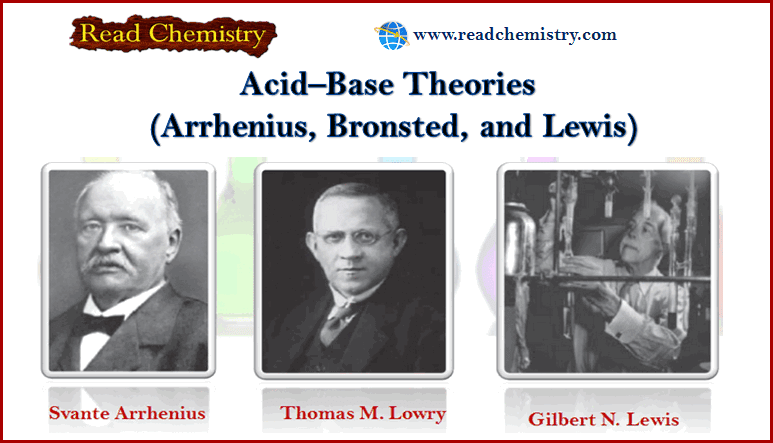
Acid-Base Theories: Arrhenius, Lewis, and Bronsted-Lowry Theory
– In this subject, we will discuss Acid-Base Theories: Arrhenius, Lewis, and Bronsted-Lowry Theory Acid-base Theories – Several acid–base theories…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
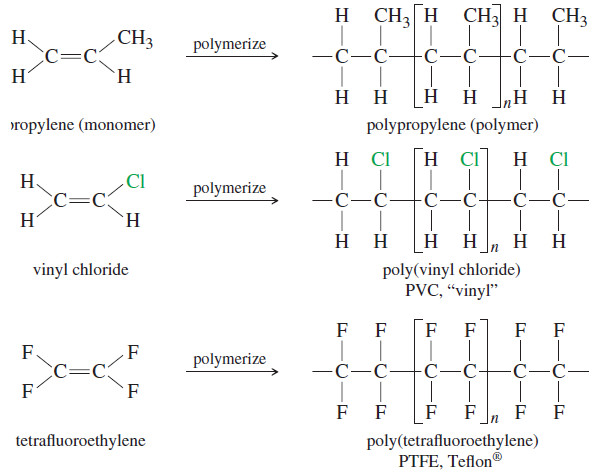
Commercial Importance of Alkenes
Commercial Importance of Alkenes – Because the carbon–carbon double bond is readily converted to other functional groups, alkenes are important…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
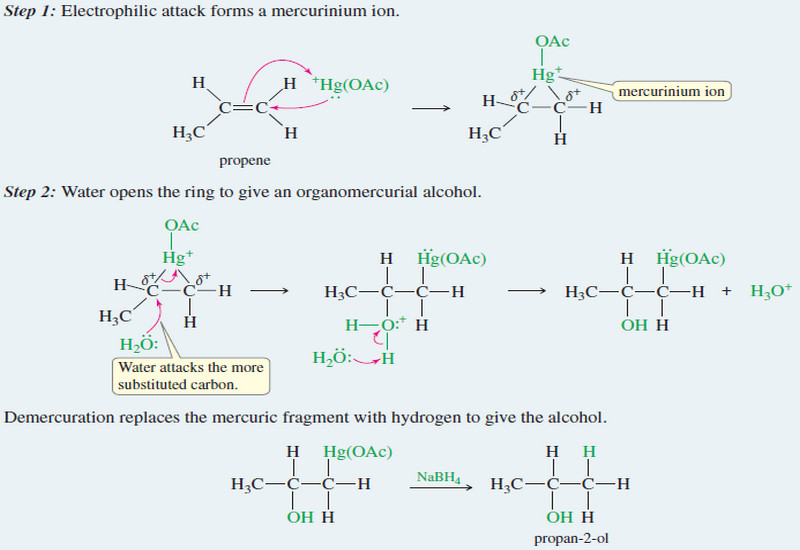
Oxymercuration–demercuration of alkenes
– Oxymercuration–demercuration of alkenes is another method for converting alkenes to alcohols with Markovnikov orientation.…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
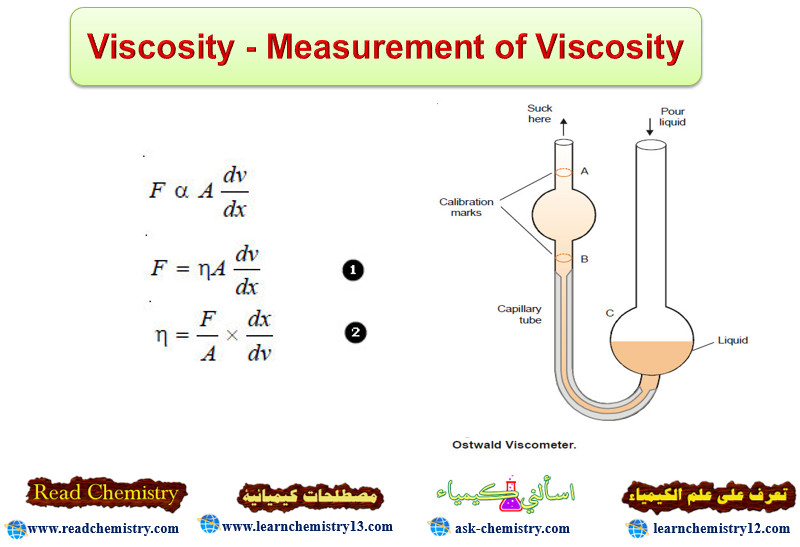
Viscosity – Measurement of Viscosity
Viscosity – Viscosity is the resistance of a liquid to flow. – A liquid may…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
Enthalpy: Heats of Reaction and Chemical Change
In this subject, we will discuss the Enthalpy: Heats of Reaction and Chemical Change. Enthalpy:…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Analytical Chemistry
Gravimetric Titrations | Definition, Calculations & Advantages
Gravimetric titrations – Mass (weight) or gravimetric titrations differ from their volumetric counterparts in that…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-