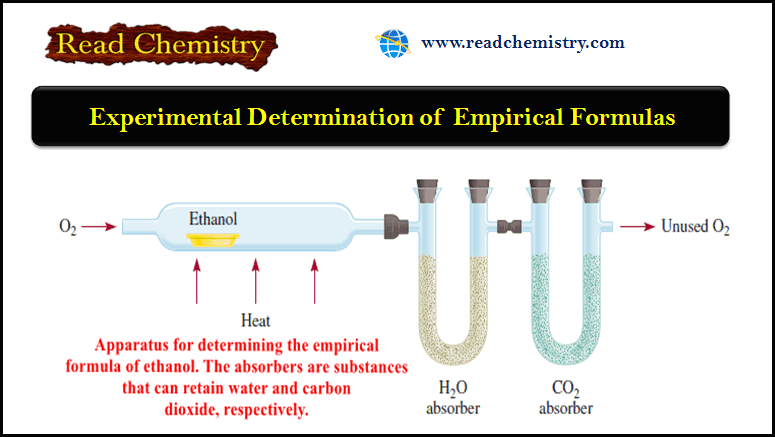
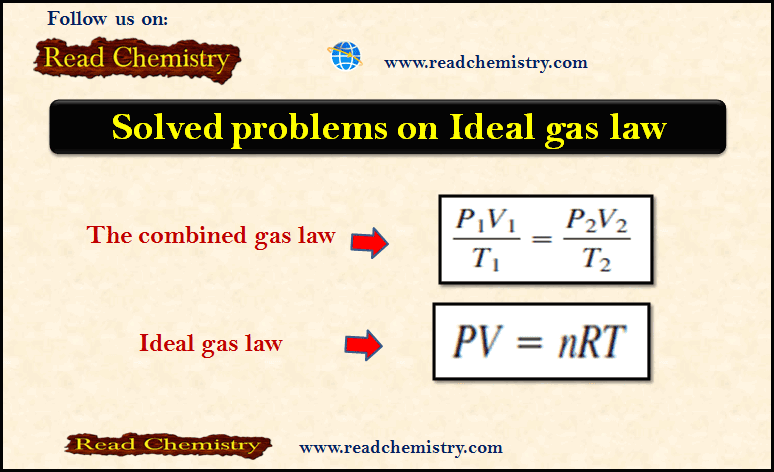
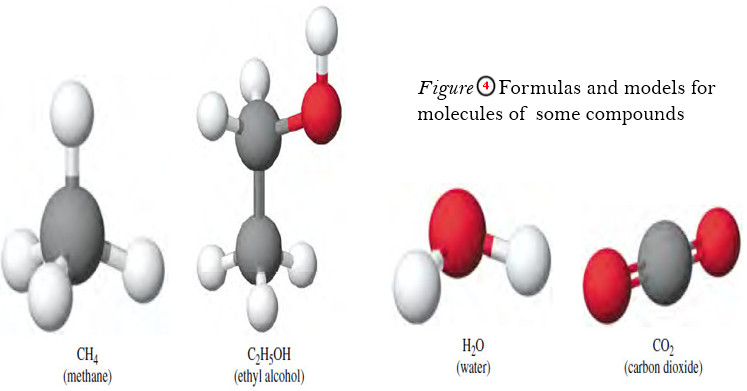
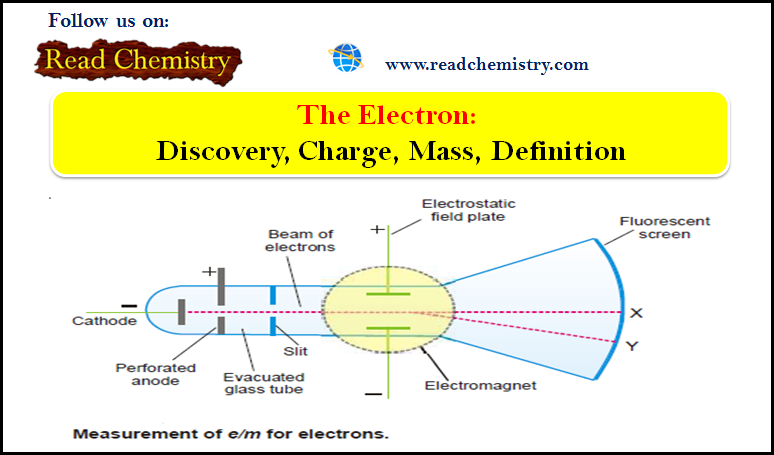
Popular Posts
-
Physical Chemistry
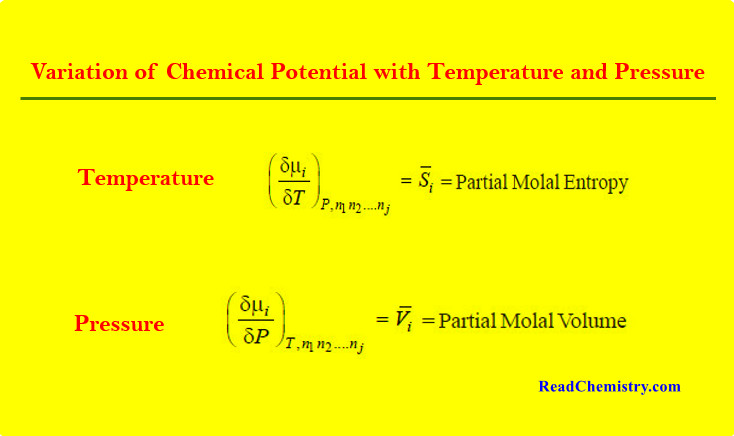
Chemical Potential
– In this topic, we will discuss The Chemical Potential and Variation of Chemical Potential with Temperature and Pressure. Partial…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
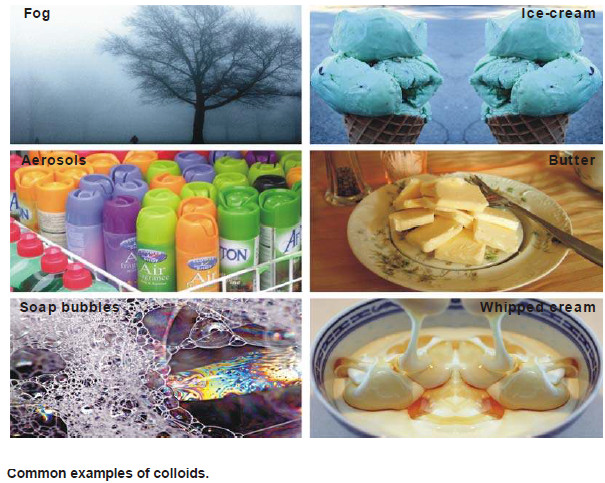
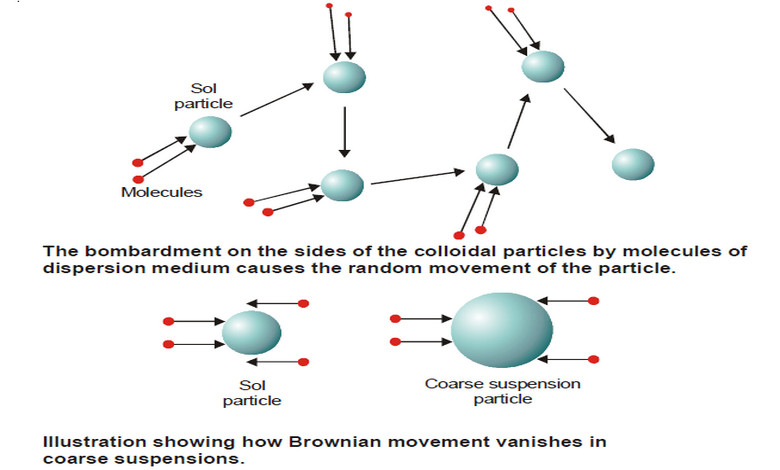
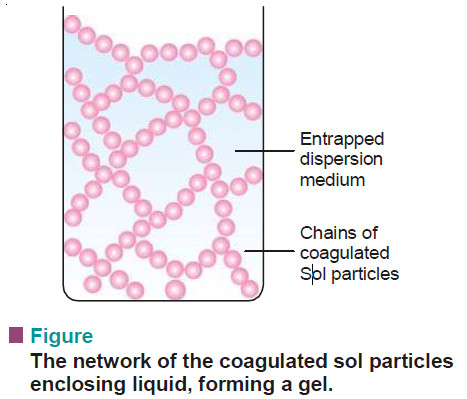
Kinetic Properties of Sols – Brownian movement
Kinetic Properties of Sols – In this topic, we will discuss Kinetic Properties of Sols. Brownian Movement – When a…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
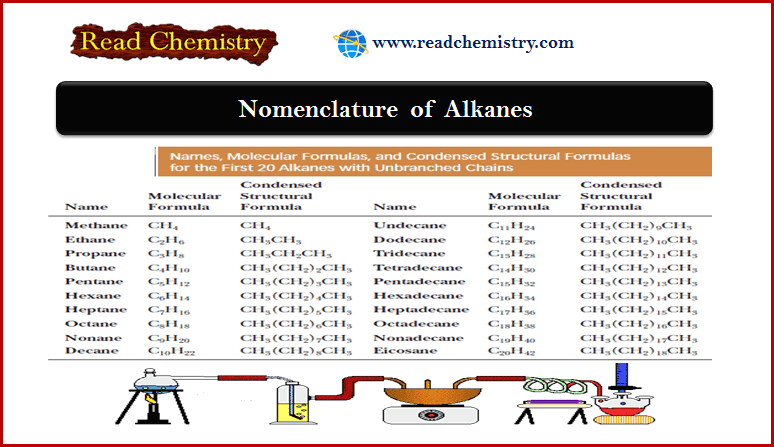
Nomenclature of Alkanes: Rules, IUPAC Name, Common Name
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nomenclature of Alkanes: Rules, IUPAC Name, Common Name What is Alkanes? –…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
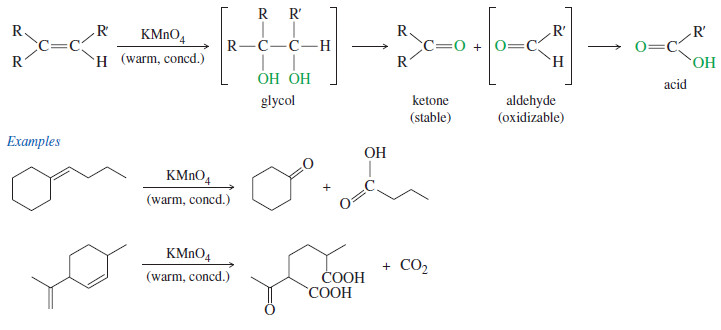
Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes
Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes Cleavage by Permanganate – In a potassium permanganate dihydroxylation, if the solution is warm or acidic…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
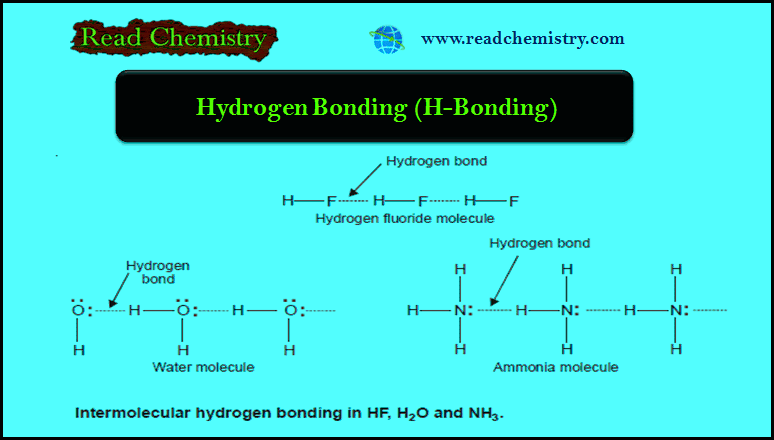
Hydrogen Bonding: Definition, types, Examples, Characteristics
– In this subject, we will discuss the hydrogen Bonding (Definition, types, Examples, Characteristics) Hydrogen Bonding (H-Bonding) – When hydrogen (H)…
Read More » -
Analytical Chemistry
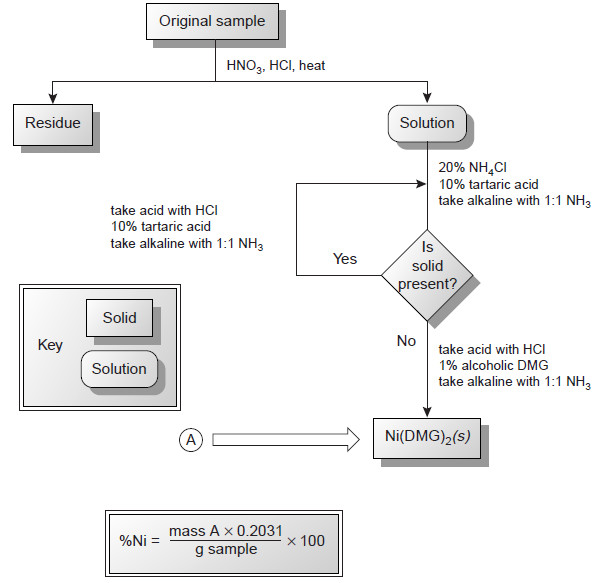
Gravimetric Titrations | Definition, Calculations & Advantages
Gravimetric titrations – Mass (weight) or gravimetric titrations differ from their volumetric counterparts in that the mass of titrant is…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
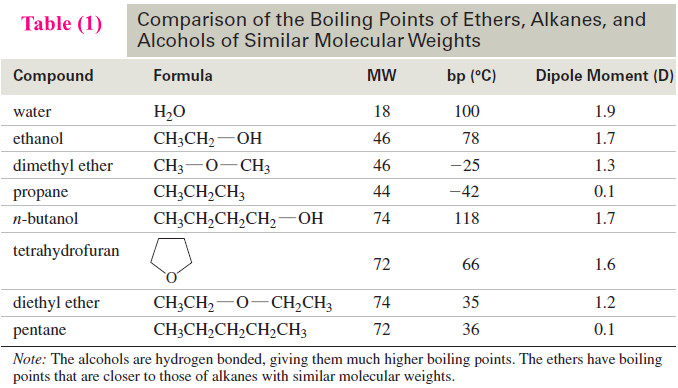
Physical Properties of Ethers
– In this topic, we will discuss The Physical Properties of Ethers. Introduction to Ethers …
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Free Download Electrochemistry book (Principles and Applications)
– In this subject, we will discuss Free Download Electrochemistry book (Principles, Methods, and Applications)…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
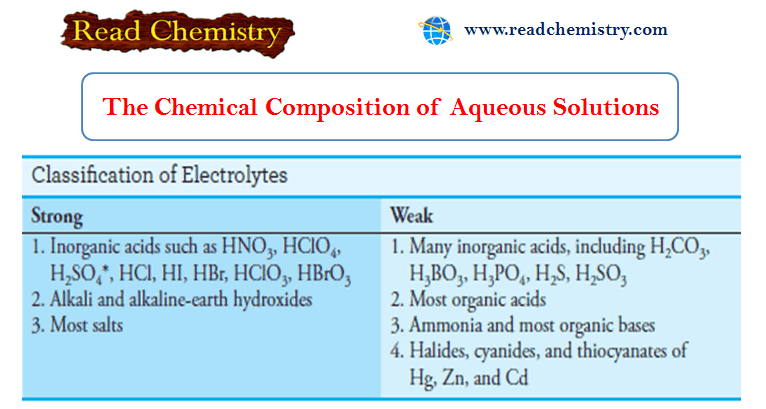
Analytical Chemistry
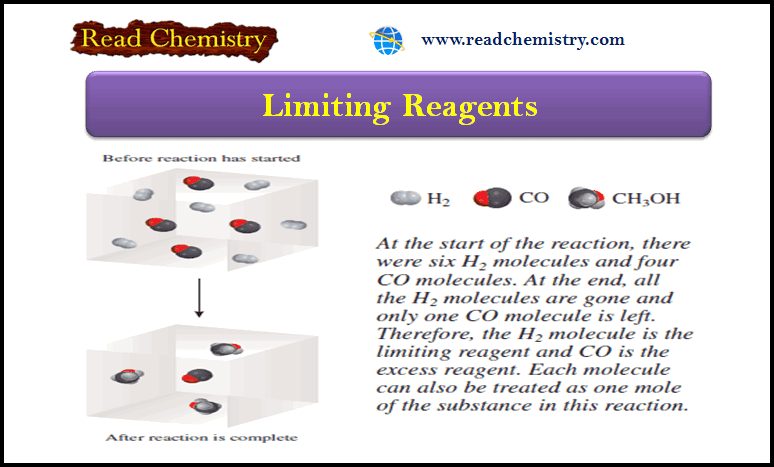
The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solution
– In this subject, we will discuss the Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solution – Water…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
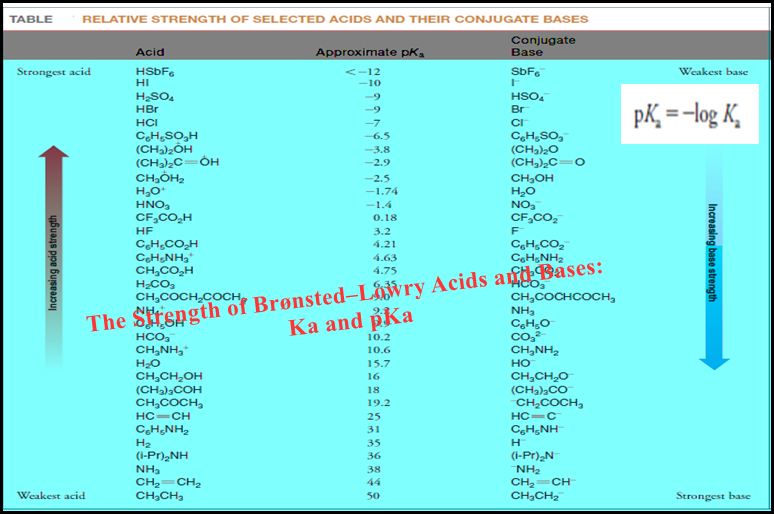
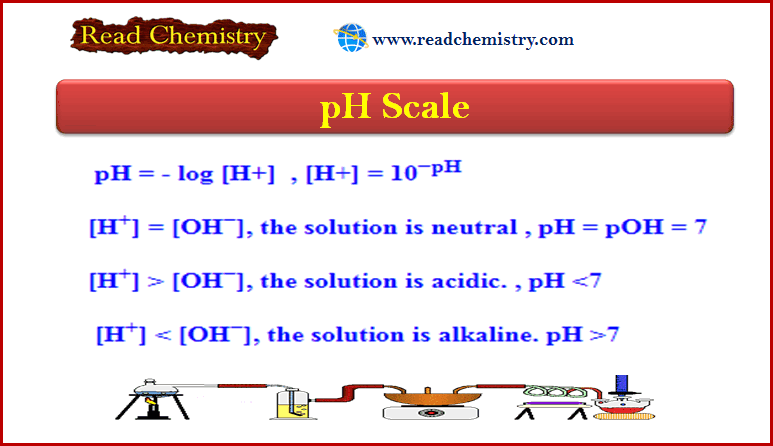
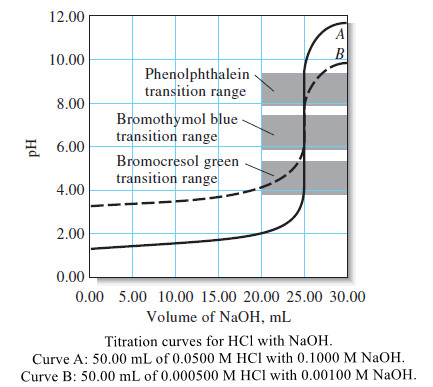
Analytical Chemistry
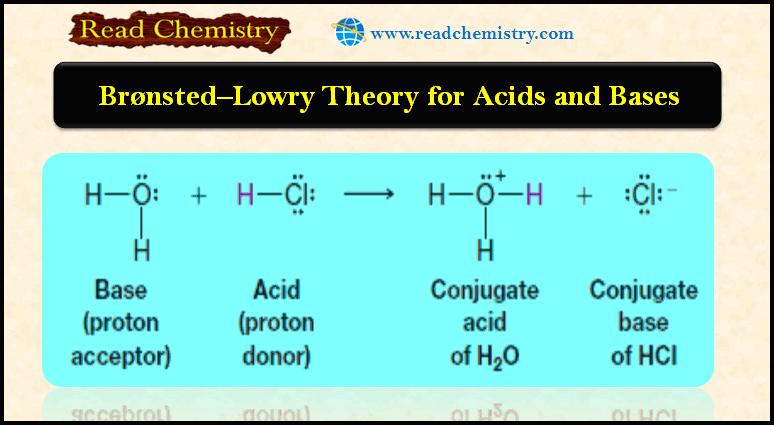
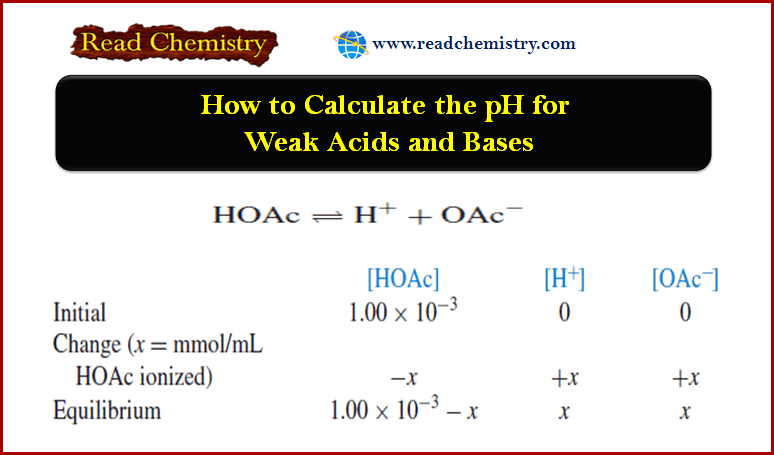
Bronsted-Lowry Acid Strength: Ka and pKa
– In this subject, we will discuss the Bronsted-Lowry Acid Strength: Ka and pKa Bronsted-Lowry…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-