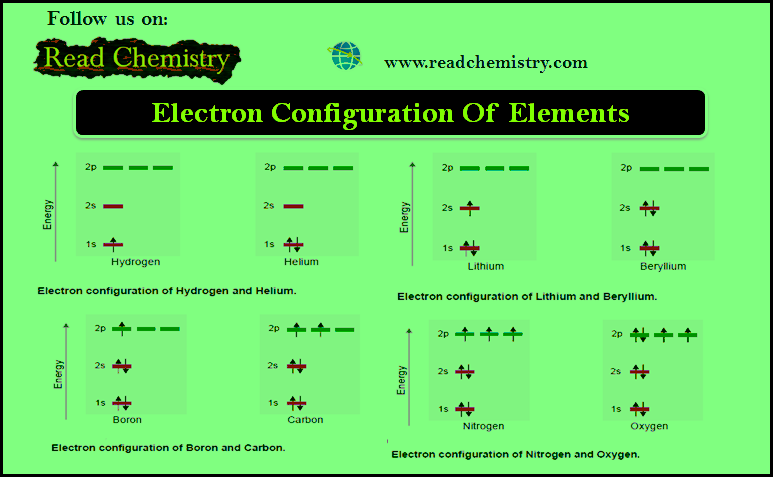
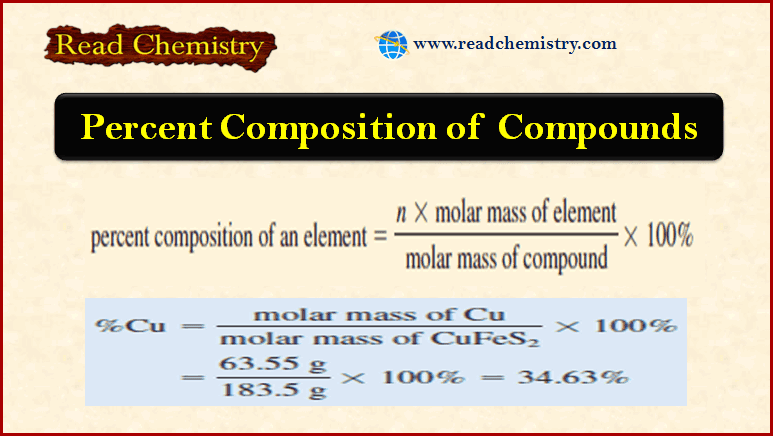
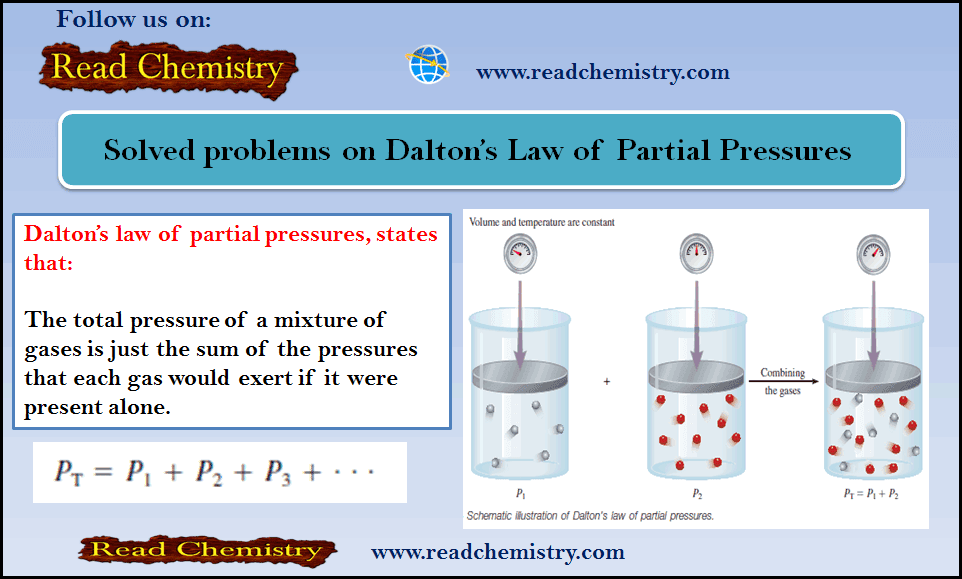
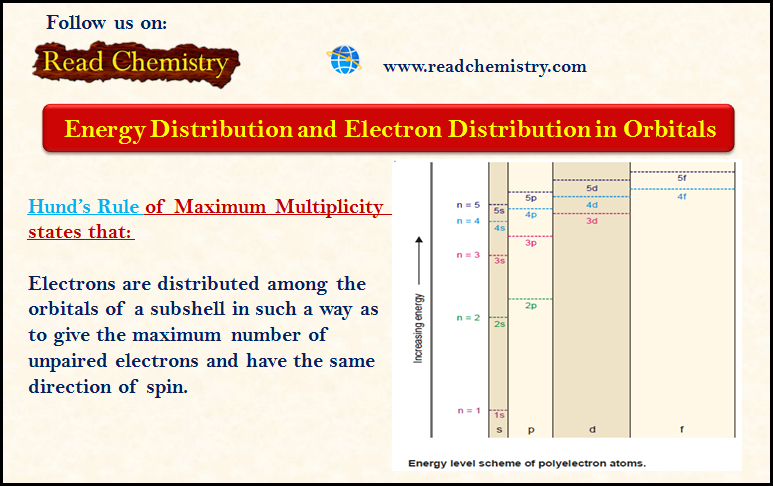
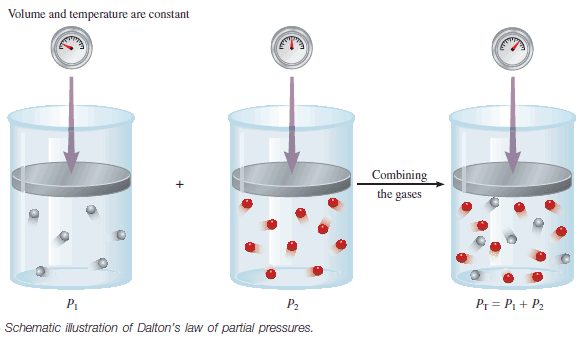
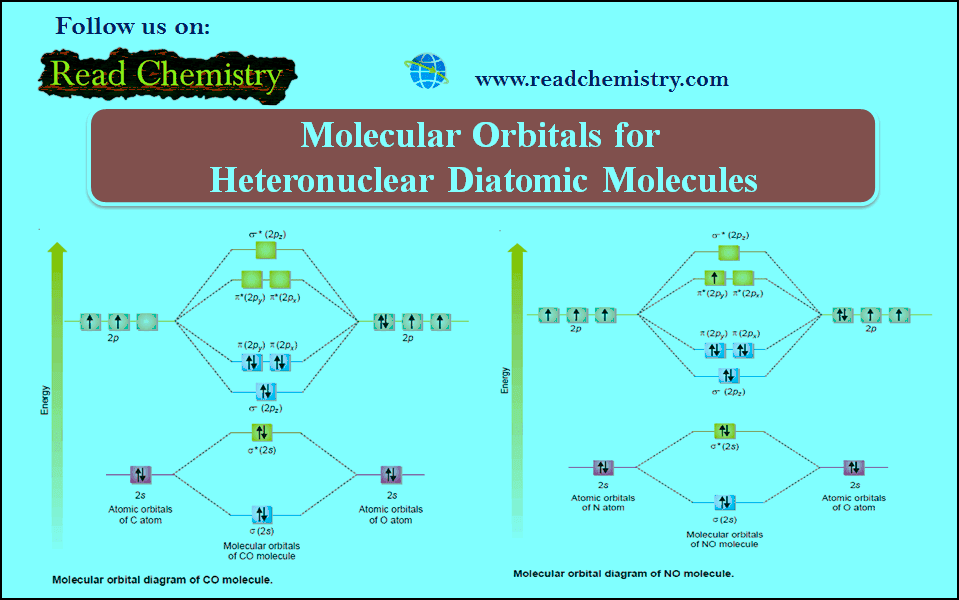
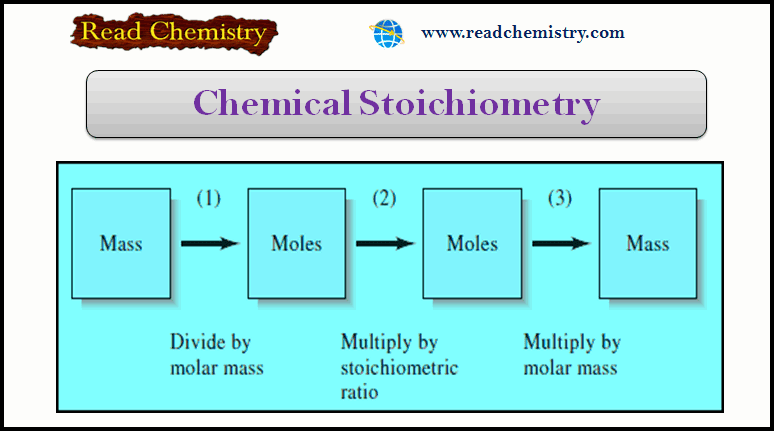
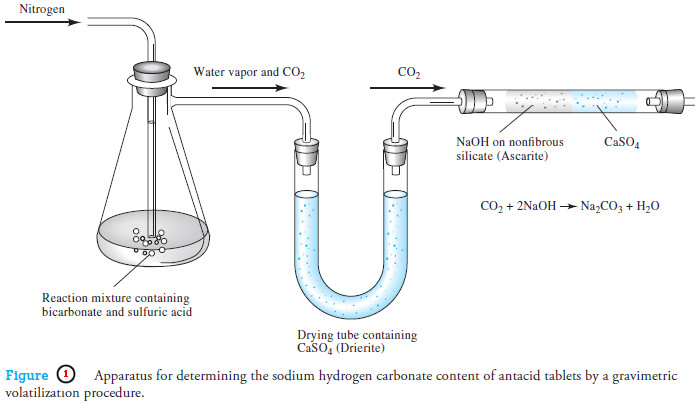
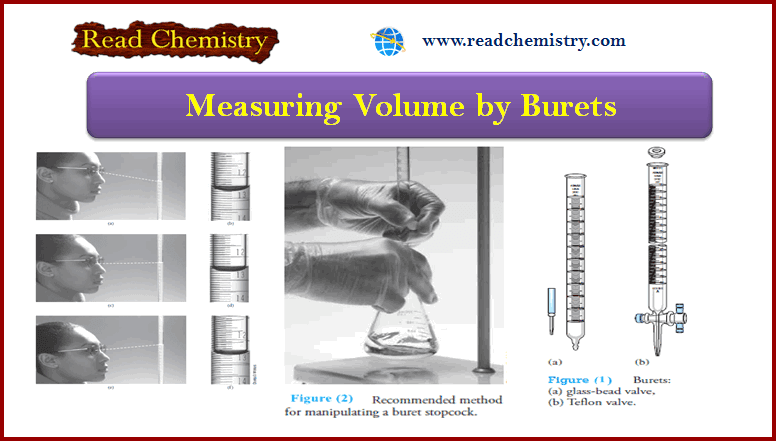
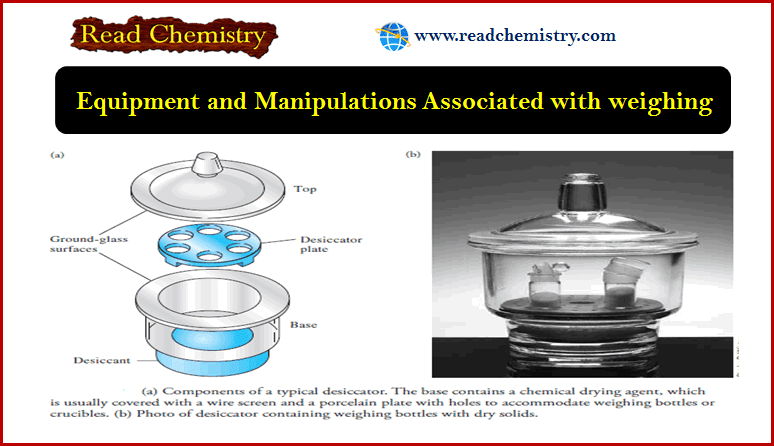
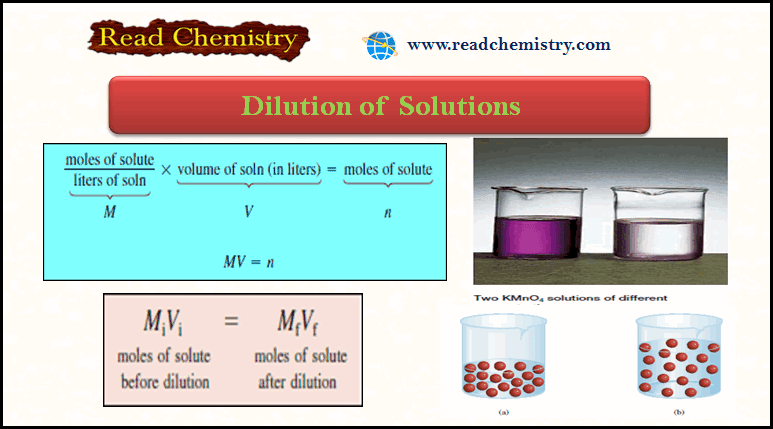
Popular Posts
-
Analytical Chemistry
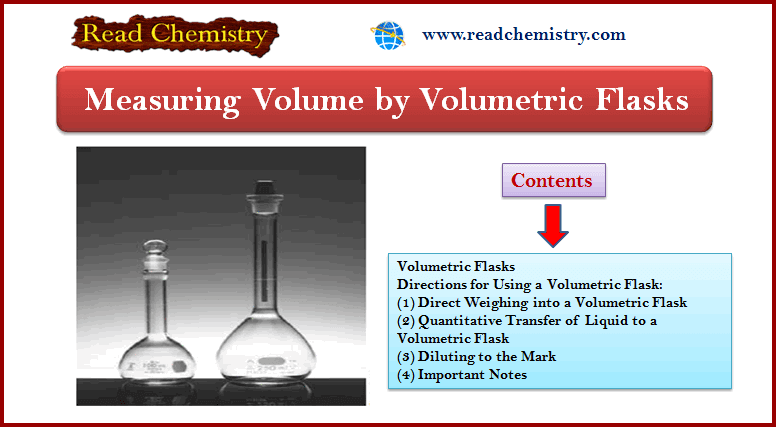
Volumetric Flask: Overview, Uses, Function
Volumetric Flask – A volumetric flask is manufactured with capacities ranging from 5 mL to 5 L and is…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
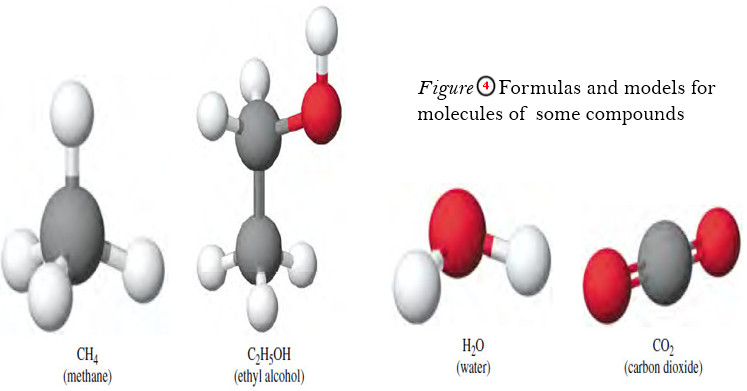
Atoms and Molecules
Democritus’s ideas about atoms – The Greek philosopher Democritus (470–400 BC) suggested that all matter is composed of tiny, discrete,…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
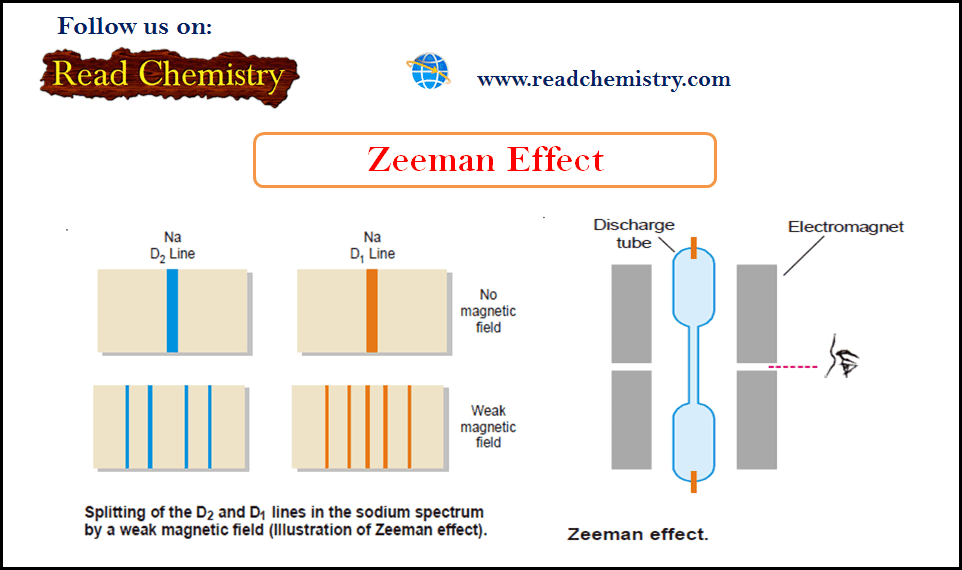
Zeeman Effect
Zeeman Effect – In 1896 Zeeman discovered that spectral lines are split up into components when the source emitting lines…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
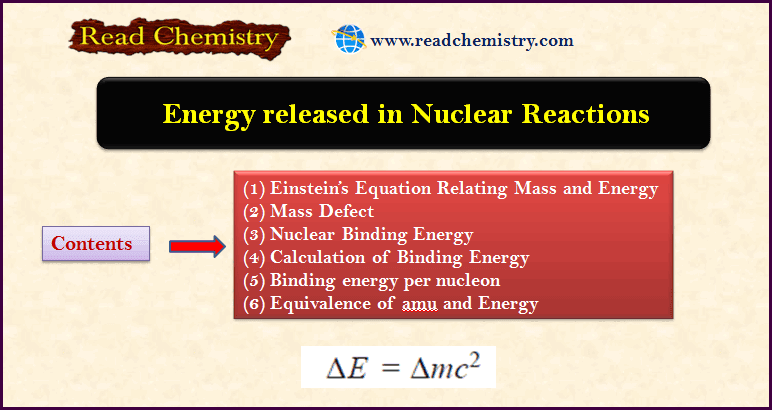
Energy released in Nuclear Reactions: Nuclear Binding Energy
– In this subject, we will discuss the energy released in Nuclear Reactions: Nuclear Binding Energy Einstein’s Equation Relating Mass and…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
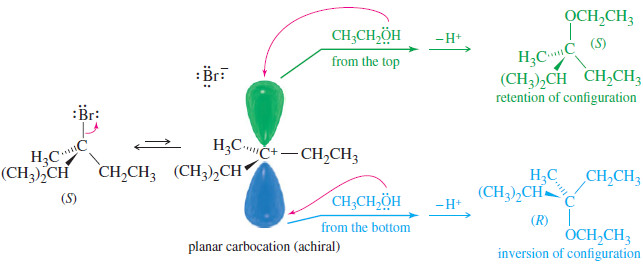
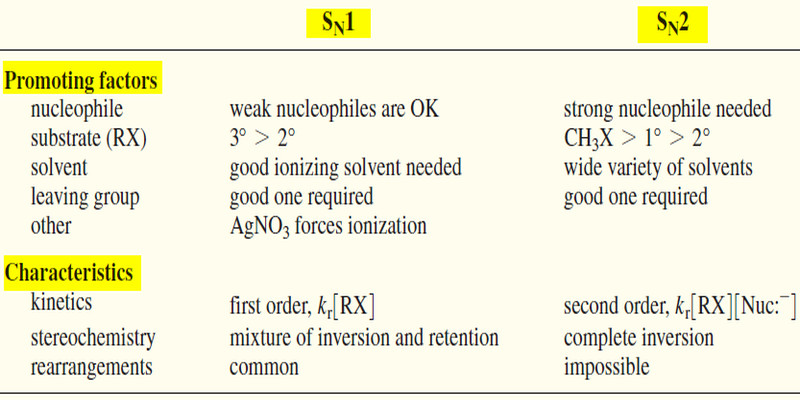
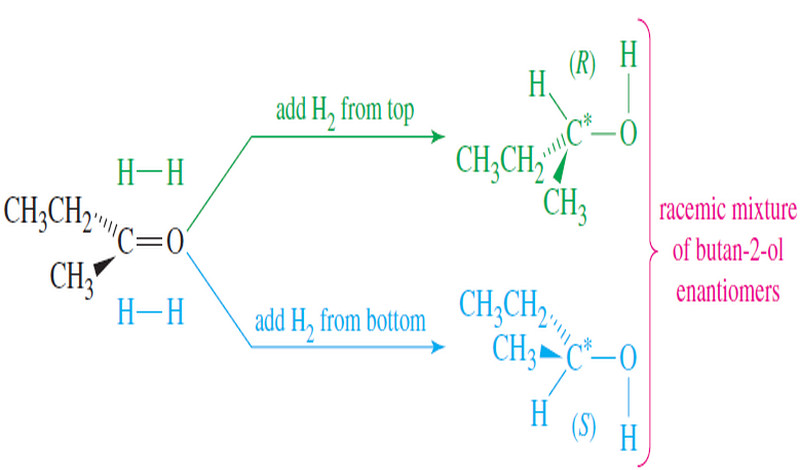
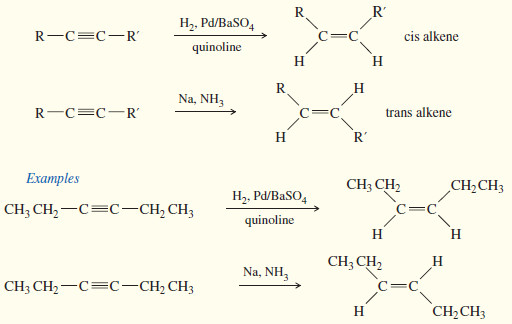
Stereochemistry of the SN1 Reactions
Stereochemistry of the SN1 Reaction – The SN2 reaction is stereospecific: the nucleophile attacks from the back side of the…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
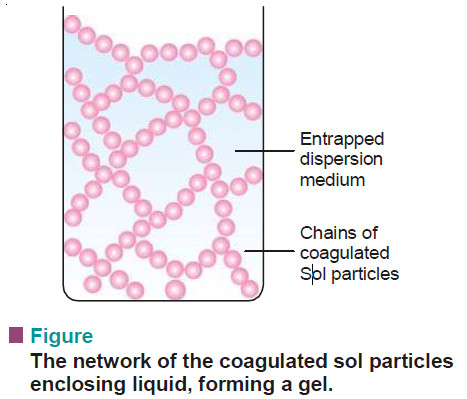
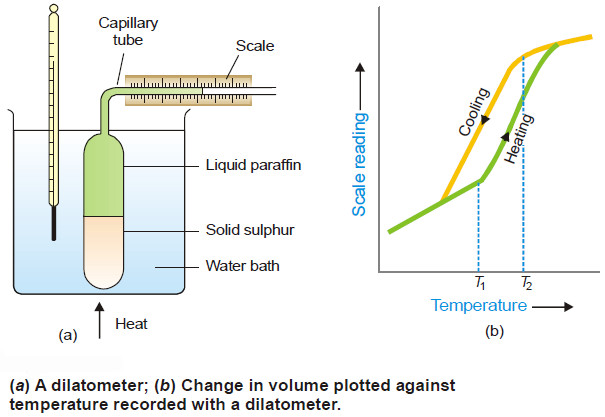
Gels : Defination, Types, Properties
– In this topic, we will discuss The Gels : Defination, Types, and Properties. What are Gels? – A gel…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
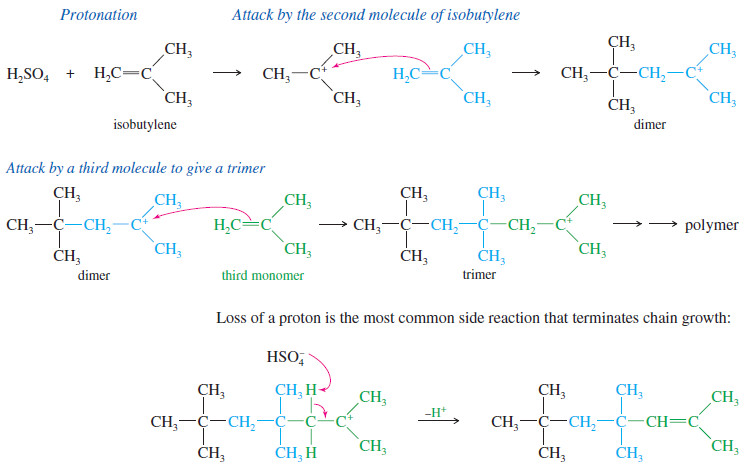
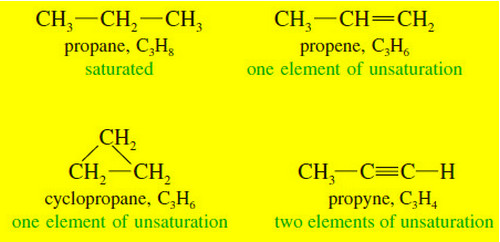
Polymerization of Alkenes
Polymerization of Alkenes – A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
Polymorphism – Allotropy
Polymorphism – The occurrence of the same substance in more than one crystalline forms is…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
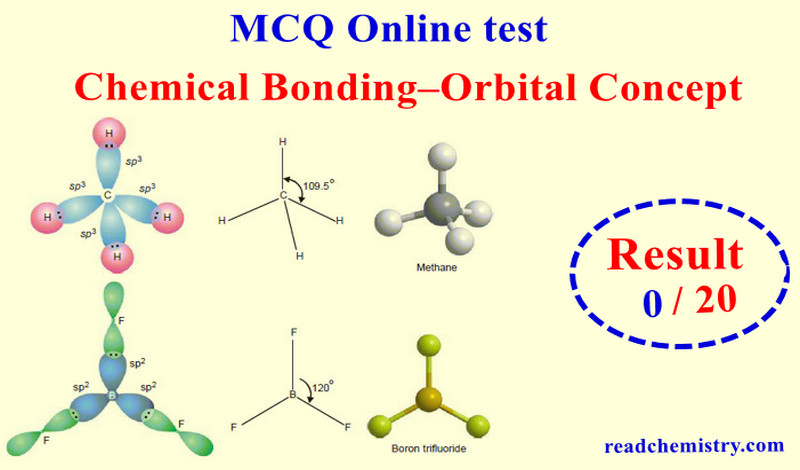
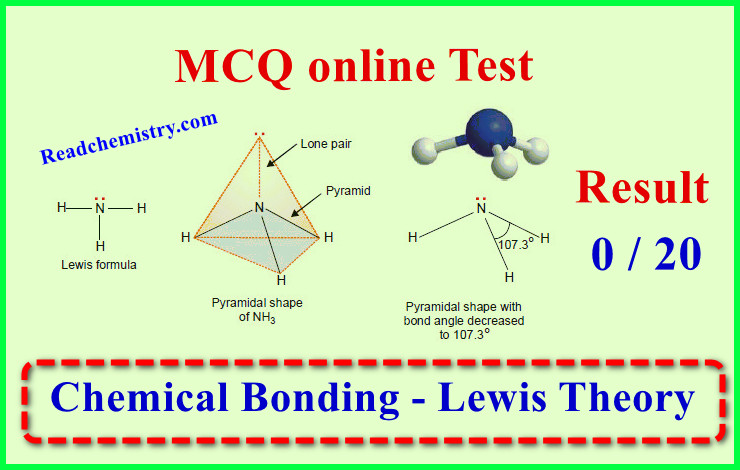
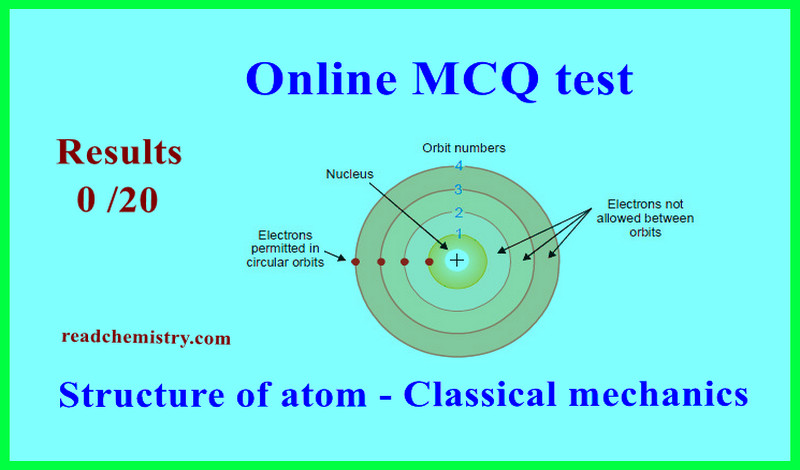
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory – In this subject, you will find 46…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Analytical Chemistry
Some Terms Used in Volumetric Titration
Some Terms Used in Volumetric Titration – A standard solution (or a standard titrant) is…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-