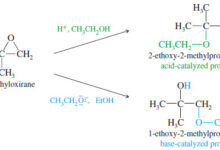
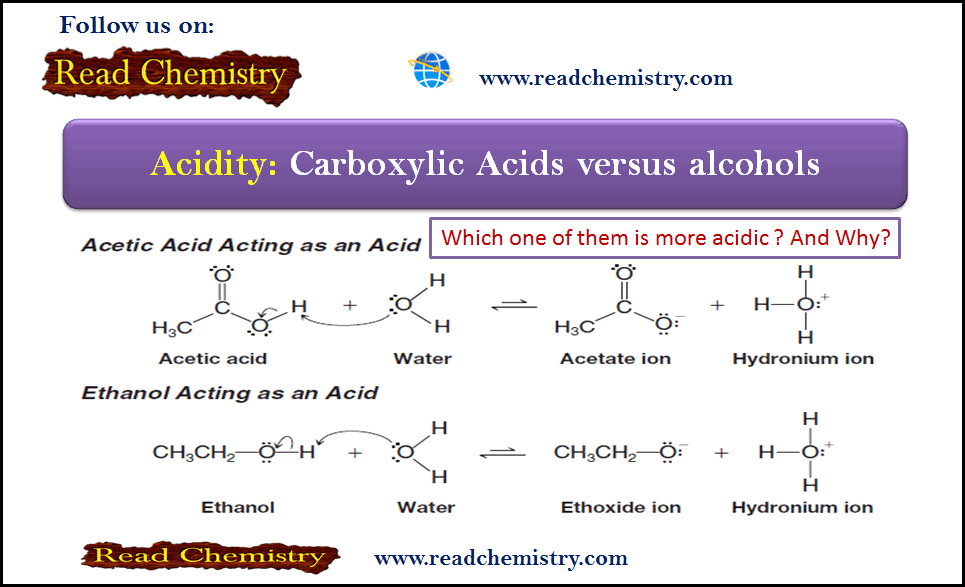
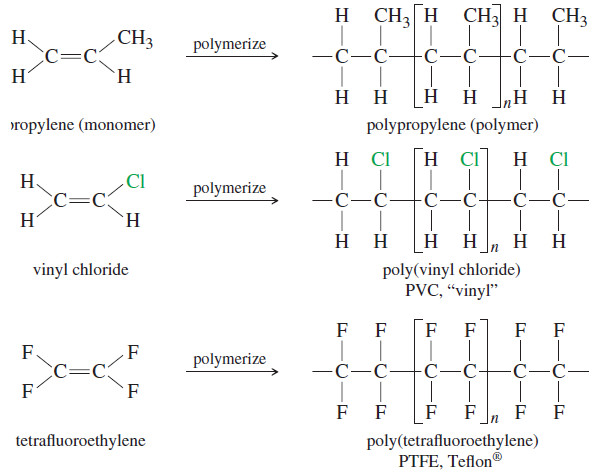
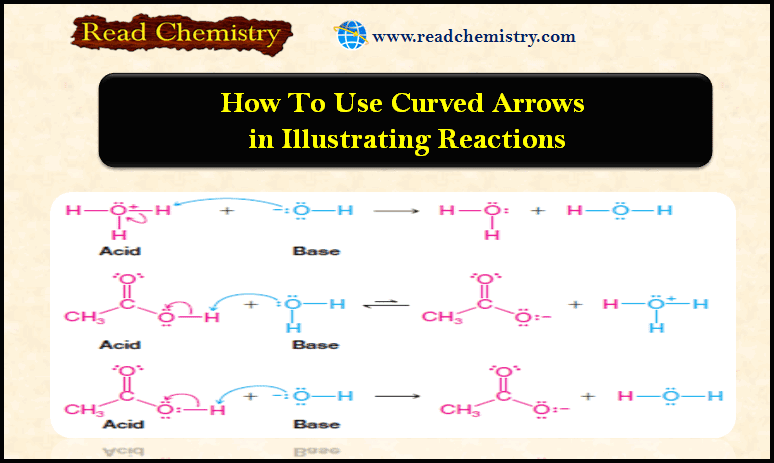
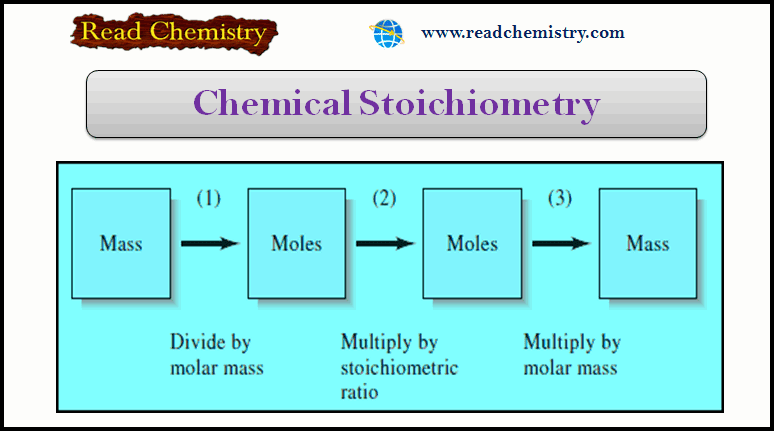
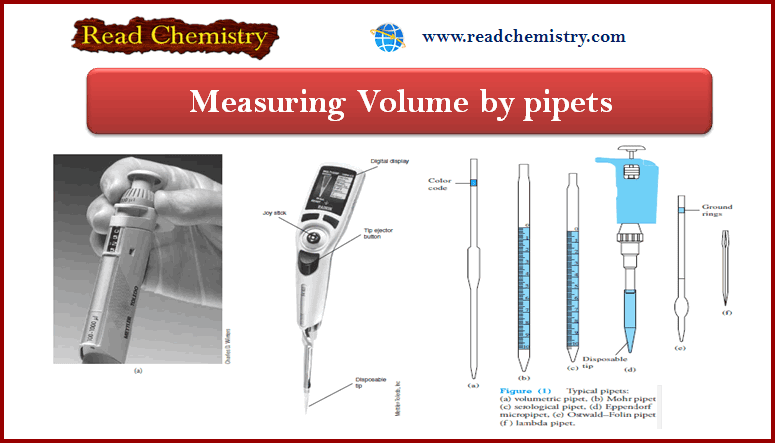
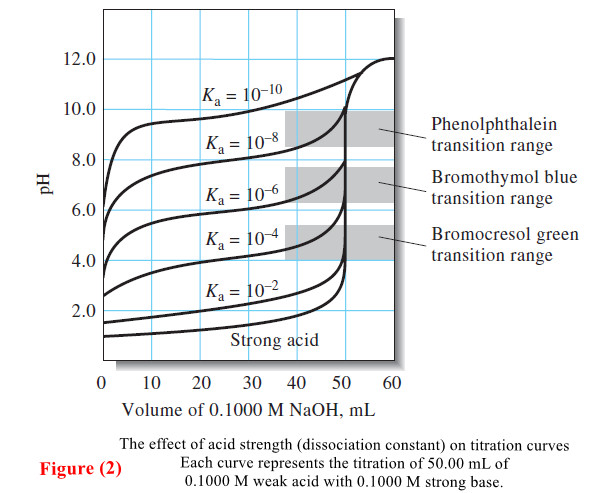
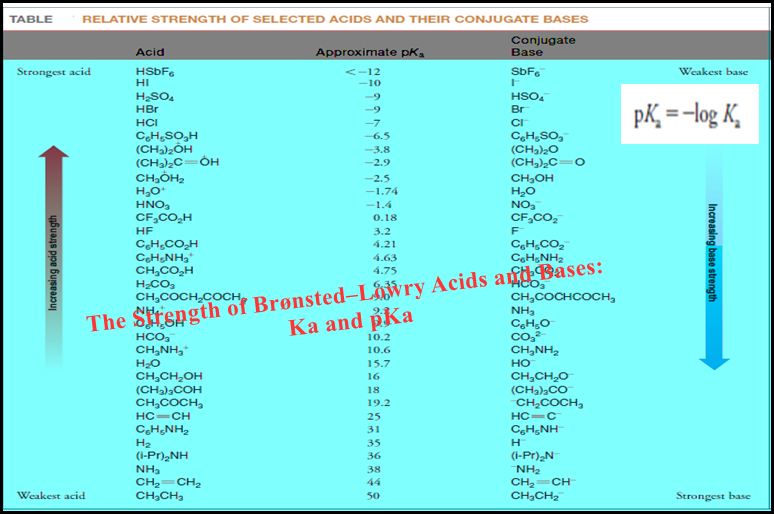
Popular Posts
-
Organic Chemistry
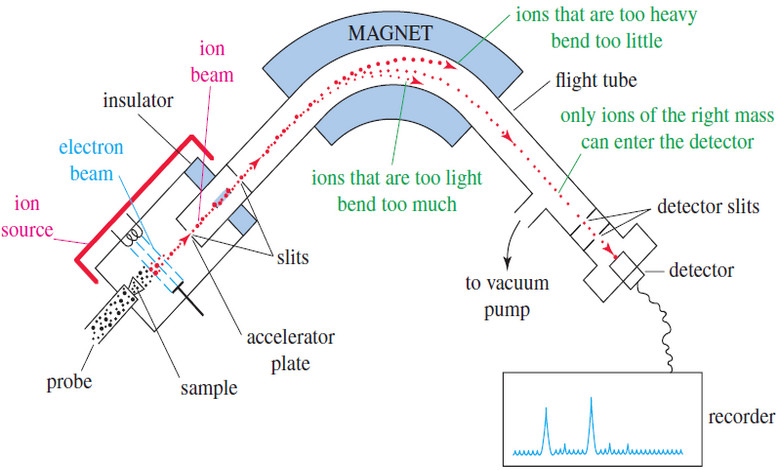
Mass Spectrometry : Introduction
Mass spectrometry (MS) provides the molecular weight and valuable information about the molecular formula, using a very small sample. Introduction…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
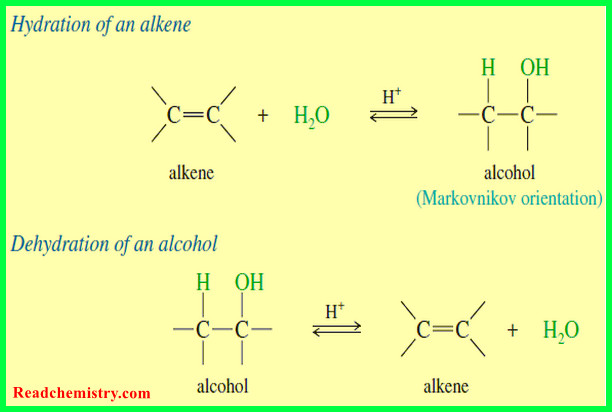
Hydration of Alkenes: Addition of Water
Hydration of Alkenes will be discussed by Addition of Water Addition of Water: Hydration of Alkenes – An alkene may…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
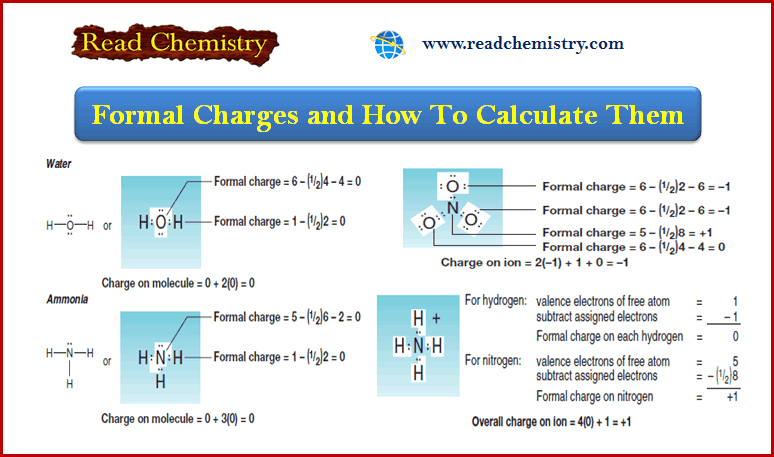
Formal Charge: Definition, Formula, Calculation, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Formal Charge: Definition, Formula, Calculation, Examples Formal Charge and How To Calculate…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
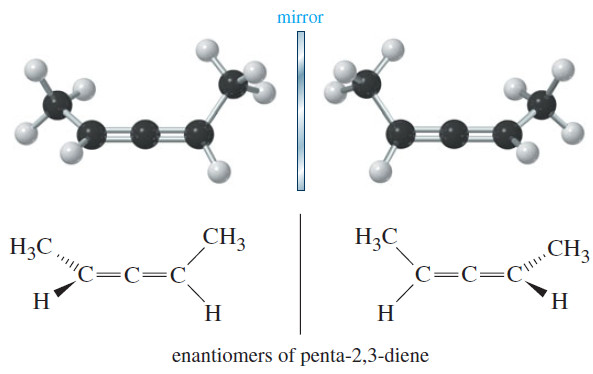
Chiral Compounds without Asymmetric Atom
Chiral Compounds without Asymmetric Atoms – Most chiral organic compounds have at least one asymmetric carbon atom. – Some compounds…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
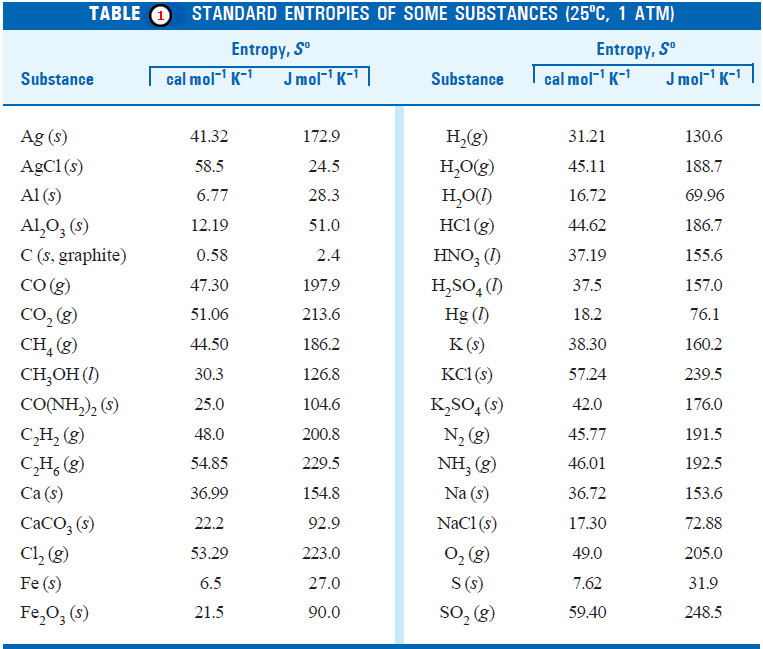
Entropy : Definition, Units, Solved Problems
Definition of entropy – Entropy is a thermodynamic state quantity that is a measure of the randomness or disorder of the…
Read More » -
Analytical Chemistry
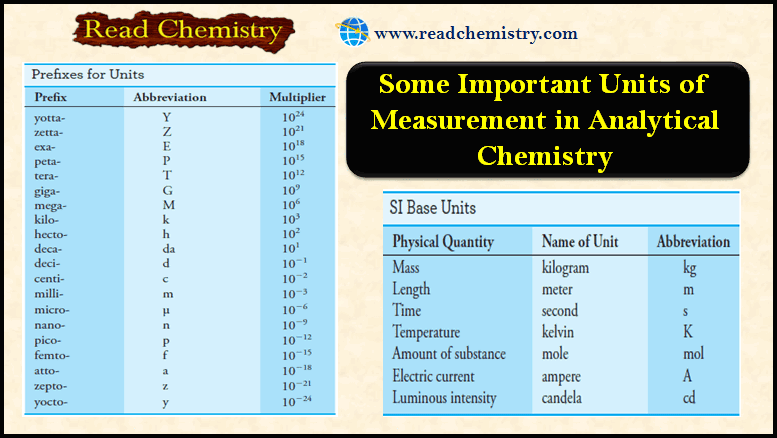
Some Important Units of Measurement in Analytical Chemistry
SI Units – Scientists throughout the world have adopted a standardized system of units known as the International…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
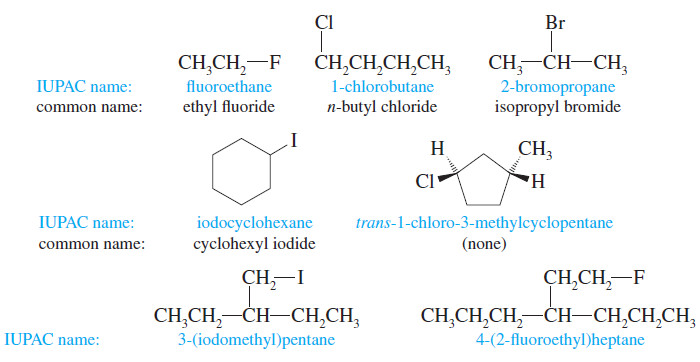
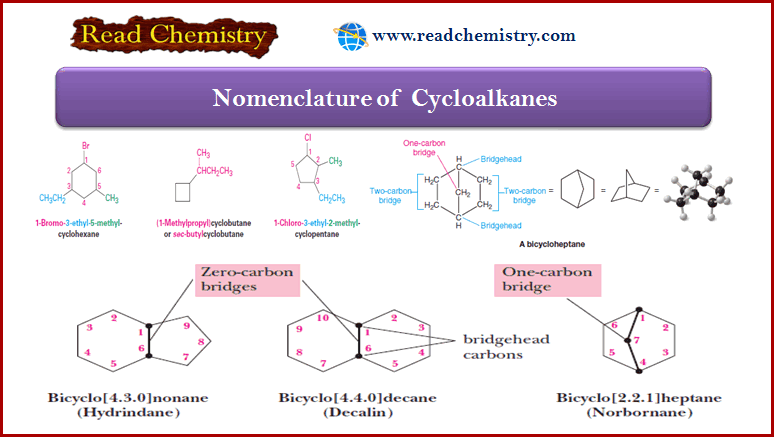
Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
Introduction to Alkyl Halides – In this subject , we consider Nomenclature of alkyl halides.…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
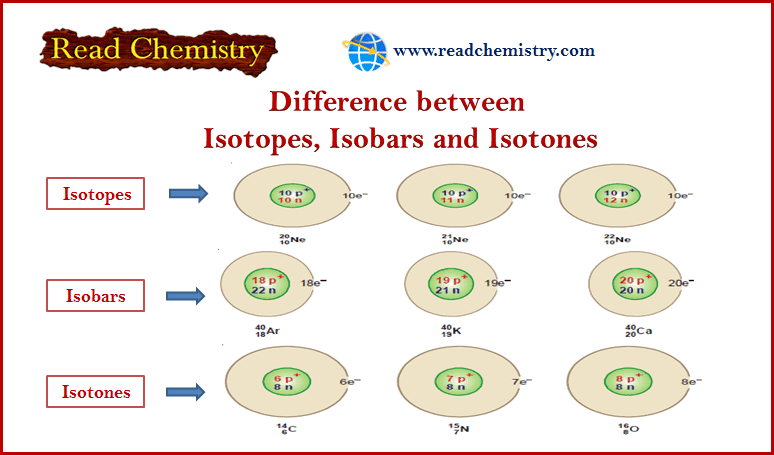
Difference between Isotopes, Isobar, and Isotones
In this subject, the Difference between Isotopes, Isobar, and Isotones will be discussed with some…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
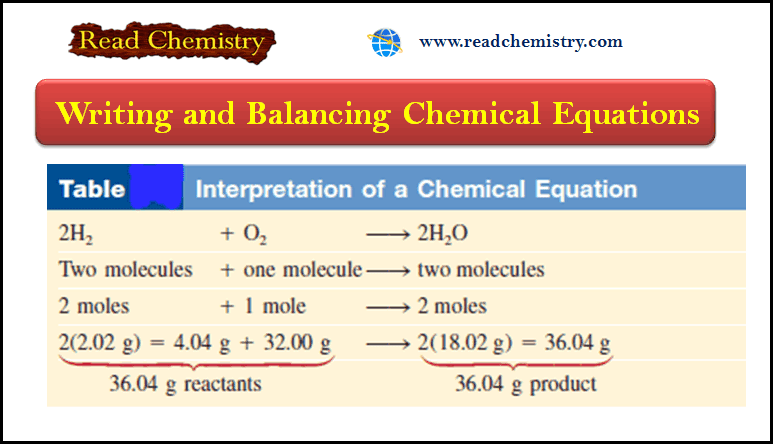
Chemical Equations – Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
– In this subject, we will discuss Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations. Chemical Reactions and…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
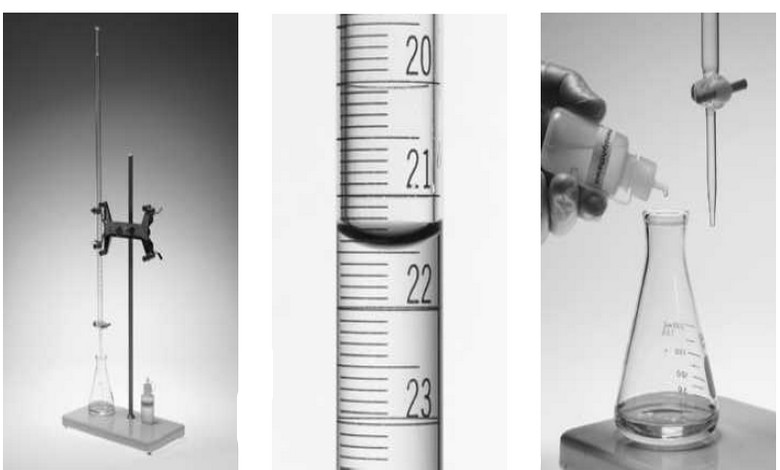
Analytical Chemistry
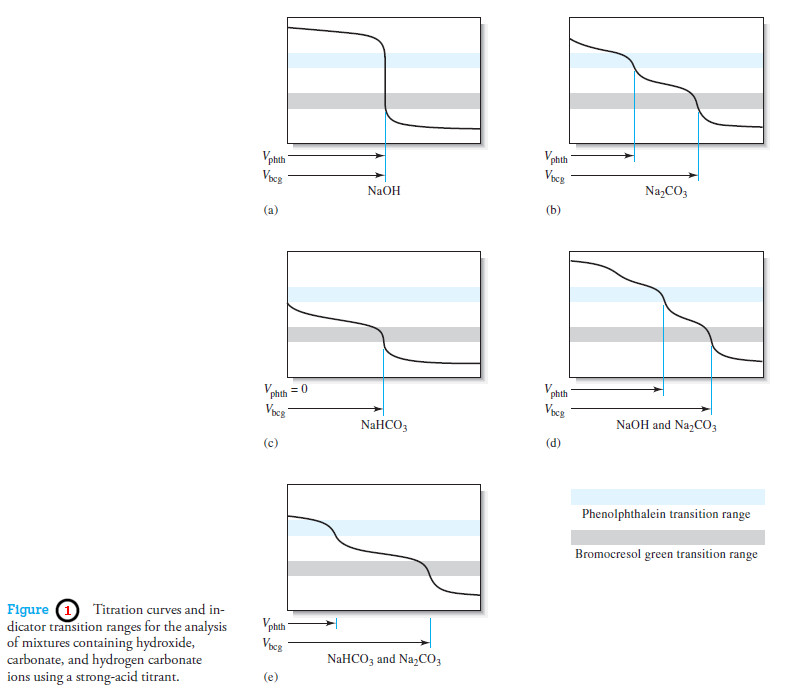
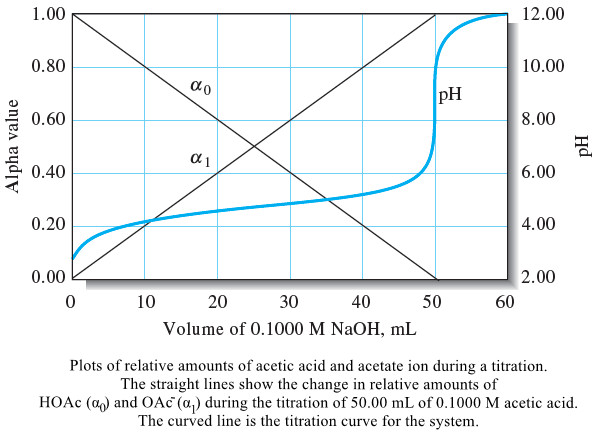
Applications of Neutralization Titrations
– In this topic, we will discuss The Applications of Neutralization Titrations. Typical Applications of…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-